High and ultrahigh resolution
molecular spectroscopy
High resolution molecular spectra contain unique information about the structure of molecules, dynamics of collective motion of nuclei and electrons in molecules, as well as about intramolecular and intermolecular interactions specified by the basic laws of quantum physics. Experimental and theoretical methods of study-
ing molecular spectra in the millimeter and submilli-meter wavelength ranges have been developed from the first days of IAP RAS establishment. The major recent achievements in this field are the following:
• Precision resonator spectroscopy has been advanced significantly. Its applications include measurements of ultra-low loss in liquid and solid dielectrics, study of the dielectric properties of thin films, reflection coefficients of highly reflective materials and coatings (V. V. Parshin, E. A. Serov); and investigation of the spectra of atmospheric gases (M. Yu. Tretyakov,
M. A. Koshelev, D. S. Makarov). The operating range of the resonator spectrometer has been expanded to the submillimeter region, and its sensitivity in wideband spectra recording has been increased by more than an order of magnitude. Addition of a pressure and temperature controlled chamber enabled high-accuracy quantitative study of the effect of collisional coupling of the lines of molecular oxygen absorption band at
60 GHz, which resulted in updating in collaboration with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology of the world-famous model of atmospheric absorption. Investigation of the humidity-related nonresonant atmospheric absorption revealed a possible way to eliminate systematic errors of all the previous similar studies caused by water molecules adsorption by the elements of the measuring resonator; most accurate todate empirical parameters of the continuum have been found in a wide temperature range. The first observation of a resolved rotational spectrum of water dimer in equilibrium conditions close to atmospheric ones was realized using this spectrometer, which permitted, in particular, to prove that water dimer formation is the main mechanism responsible for the formation of the water vapor related part of atmospheric continuum. This proved the hypothesis put forward almost half a century ago by Prof. S. A. Zhevakin of the Radio Physical Research Institute that had not been confirmed despite numerous considerable efforts.
| |
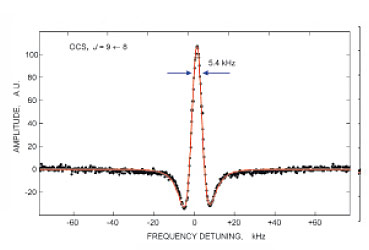 |
Example of Lamb dip record on rotational transition line
of carbonyl sulfide molecule
|
• A broad-band millimeter and submillimeter wavelength video spectrometer has been developed that provides narrow nonlinear resonances with a mi-nimum width of 10.6 kHz within the Doppler contour of molecular absorption lines using the Lamb dip method and measurement of their frequencies with absolute accuracy of 500 Hz (S. P. Belov, G. Yu. Golubyatnikov). These are Russia's record parameters corresponding to the best world standards.
• High-accuracy analysis of the line shape of carbonyl sulfide molecule (OCS) rotational spectrum observed in experiment permitted solving the decades-discussed problem of which of the numerous proposed models of line profile corresponds to the processes occurring during collisional interaction of molecules and, therefore, is most suitable for high-accuracy modeling of radiation absorption in gases of polar molecules
(M. A. Koshelev in collaboration with researchers of the Lille and Paris Universities, France).
• The theoretical methods of calculating molecular spectra developed at IAP RAS on the basis of variational computations (O. L. Polyansky, N. F. Zobov,
R. I. Ovsyannikov in cooperation with the University College London) have attained a new level of accuracy. Global estimates of the vibrational-rotational spectrum of vital water molecules have been made. The accuracy of calculations of frequencies of all lines throughout the energy range (from the low-lying rotational levels to the dissociation energy) is more than six significant digits, and the prediction of the line position is within the line contour observed in traditional experiments. The achieved accuracy of the line intensity calculation exceeds the accuracy of the experiment. Ab initio calculations of the spectrum of the simplest triatomic molecule — H3+ ion that plays an important role in astrophysics and atmospheric chemistry were done with record accuracy. The calculated line frequencies agree with the experimental ones up to five significant digits.
A pioneer approach to the description of intramolecular dynamics based solely on the symmetry principles was developed by A. V. Burenin. Within this approach, the configuration space of the molecule is not used in explicit form; hence, the wave functions of the space coordinates are not considered explicitly. But it is thanks to its basic difference from traditional methods that the developed approach is currently the only one capable of solving a number of topical problems of the internal molecular dynamics. First of all, it allows description of nonrigid molecules with several equilibrium configurations. The resulting models are rigorous and a purely algebraic computation scheme may be employed. The results of the research were presented in the well-known monograph "The Symmetry of Quantum Intramolecular Dynamics" that went through three editions (Institute of Applied Physics, 2002, 2006
and 2012). In November 2012 the book was published in the English language (DeGruter, Germany).
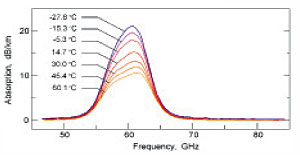 |
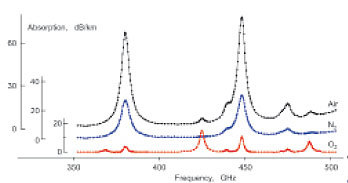 |
Experimental records of atmospheric oxygen absorption band at different temperatures made with record
high sensitivity
|
First microwave broadband records of absorption
spectrum of principal atmospheric gases mixed
with water vapor
|





